
A Guide to Pan-Tilt Positioners: Features, Selection, and Use Cases
In industries where precision monitoring and remote control are critical, pan-tilt positioners play a vital role. From defence surveillance and border security to industrial and offshore monitoring, these systems provide smooth, accurate control of cameras, sensors, and antennas. By enabling wide coverage, flexible movement, and reliable positioning, pan-tilt positioners help operators make better decisions in real time.
This guide will break down what pan-tilt positioners are, their key specifications, how to select the right one, and the industries where they are most widely used.
What is a Pan-Tilt Positioner?
A pan-tilt positioner (PTP) is a mechanical device designed to control the orientation of equipment, usually cameras, sensors, or antennas.
- Pan refers to horizontal rotation (side to side).
- Tilt refers to vertical movement (up and down).
Unlike consumer-grade pan-tilt camera heads, industrial-grade positioners are built to handle higher payloads, extreme environments, and continuous operation. They are widely used in security, defence, marine, and industrial automation systems.
Key Features and Specifications of Pan-Tilt Positioners
When evaluating pan-tilt positioners, engineers and system integrators usually focus on the following parameters:
1. Pan Speed & Pan Angle
- Range: Many models offer full 360° continuous rotation, while others may be limited to specific arcs.
- Speed: High-speed panning (up to 100°/s or more) is ideal for target tracking, while lower speeds suit detailed inspections.
2. Tilt Speed & Tilt Angle
- Range: Typically from -90° (downward) to +90° (upward), though some advanced systems allow greater movement.
- Speed: Precision tilt control ensures stable monitoring in inspection applications, whereas faster tilt speeds are crucial in surveillance.
3. Payload Capacity
- Determines how much equipment the positioner can carry.
- Payloads range from a few kilograms (for lightweight cameras) to over 200 kg (for radar, laser range finders, zoom lenses, thermal cameras, or multiple sensors).
- A mismatch between payload and positioner capacity can lead to performance issues or mechanical wear.
4. Material & Durability
- Most positioners are built with aluminium or stainless steel (explosion proof) to be used in extreme conditions.
- Outdoor models feature IP ratings – IP67 or IP68, ensuring resistance to dust, rain, and water immersion.
- Marine-grade versions often include corrosion resistance for offshore and coastal applications.
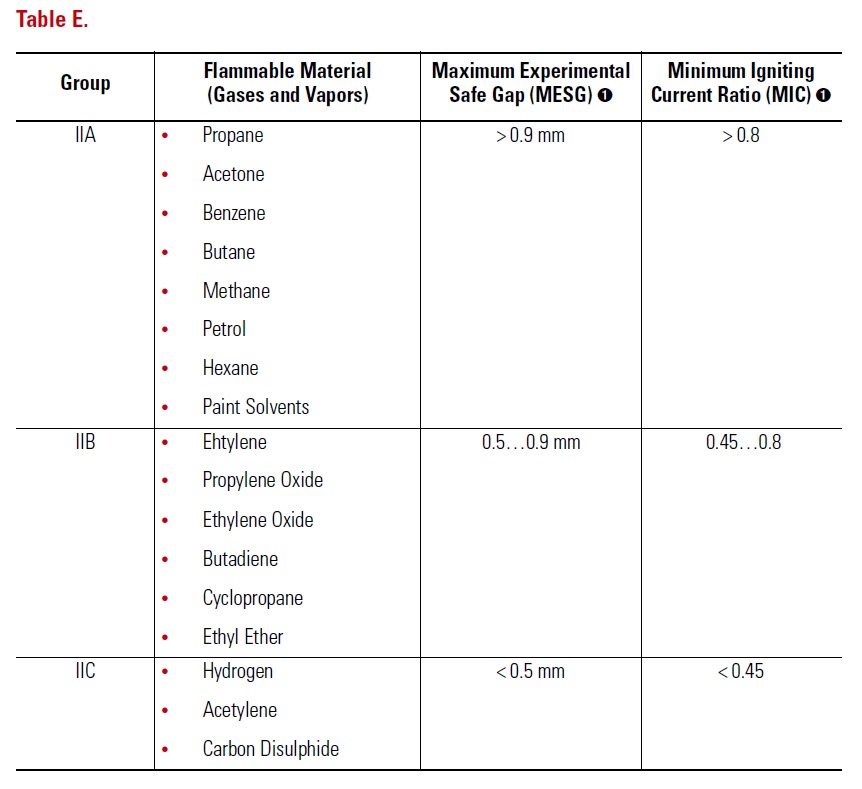
5. Explosion-Proof Design
- These positioners are used in oil & gas, petrochemicals, mining, and offshore platforms where flammable gases, vapors, or dust exist.
- In hazardous Zones 0, 1, and 2 (IEC/NEC), explosion-proof certification is required to prevent ignition.
- They use flame-proof enclosures that contain sparks or heat, ensuring the surrounding atmosphere remains safe.
- Certification follows standards such as IEC 60079 and ATEX, covering gas groups IIA, IIB, and IIC.
- Typical uses include cameras and sensors in refineries, chemical plants, paint shops, and offshore rigs.
Zone Hazardous IIA,IIB & IIC
6. Control & Integration
- Operated via joysticks, control software, or automated tracking systems.
- Support for communication protocols such as RS485, ONVIF, or Ethernet/IP.
- Can integrate with AI-based analytics for auto-tracking.
How to Select the Right Pan-Tilt Positioner
Choosing a pan-tilt positioner depends on the application environment, payload, and performance requirements.
Indoor vs. Outdoor Use
Indoor models focus on smooth, precise movement in controlled environments like labs or production floors. Outdoor versions, however, are built to resist rain, dust, and extreme temperatures, often with IP67 protection and corrosion-resistant finishes. If your system operates in harsh conditions, outdoor-grade durability is a must.
Payload Weight
Every positioner is designed for a specific weight range, and exceeding it can cause unstable performance. It’s not just the total weight but also how the payload is balanced that matters. A correctly matched payload capacity ensures smooth movement, accurate tracking, and long-term reliability.
Speed vs. Accuracy
High-speed scanning is vital for security and surveillance, where tracking fast-moving objects is key. In contrast, inspection tasks demand slower, precise positioning to capture fine details. Choosing the right balance prevents paying for unnecessary speed or sacrificing accuracy.
Environmental Conditions
The environment plays a big role in selection. Extreme heat, freezing cold, or marine saltwater exposure requires special builds with heaters, resistant coatings, or stainless-steel housings. Matching the positioner to its surroundings ensures dependable performance and longer service life.
Integration Needs
A positioner should work seamlessly with your existing control systems and monitoring software. Compatibility with common protocols like RS485, ONVIF, or Ethernet simplifies setup and ensures flexibility. The right integration saves time and makes future upgrades easier.
Certifications & Compliance
For use in hazardous environments, pan-tilt positioners must comply with international safety standards. ATEX certification (ATmosphères EXplosibles) is the most recognized in Europe, ensuring equipment can safely operate in explosive atmospheres. Globally, IECEx and NEC/CEC Class & Division approvals are also common, covering design, temperature ratings, and protection methods. Choosing certified equipment guarantees both regulatory compliance and safe, reliable performance in industries like oil & gas, mining, and chemical processing.
Industries and Systems Using Pan-Tilt Positioners
Pan-tilt positioners are widely used across diverse sectors:
Security & Surveillance
Pan-tilt positioners enable wide-area coverage for applications like border monitoring, smart city projects, and critical infrastructure security. Their fast movement and long-range precision make them ideal for 24/7 surveillance.
Defence & Aerospace
In defence systems, they are used to control thermal cameras, radar units, and electro-optical payloads. They also play a vital role in UAV ground stations where stable and accurate positioning is critical.
Industrial Inspection
Industries rely on positioners for tasks like weld inspection, process monitoring, and checking hazardous zones. Their precise movement allows for continuous and safe monitoring without manual intervention.
Broadcasting & Media
Broadcasters use them to automate smooth panning and tilting during outdoor events and live-streams. This ensures professional-quality footage while reducing manual camera handling.
Marine & Offshore
On ships and offshore platforms, positioners support cameras and sensors that must withstand salt spray, wind, and constant vibration. They ensure reliable monitoring in challenging marine environments.
Scientific & Research
Researchers use pan-tilt systems to position meteorological instruments, track wildlife, or monitor environmental conditions. Their flexibility allows accurate data collection in field studies and remote sites.
Applications of Pan-Tilt Positioners (In Detail)
Remote Visual Inspection
Pan-tilt positioners allow cameras to monitor confined or hazardous spaces without putting workers at risk. They are commonly used in power plants, chemical facilities, and underground tunnels.
Border Security
Equipped with long-range zoom and thermal cameras, positioners provide 24/7 border surveillance. Their wide coverage and rapid tracking make them vital for detecting movement across large perimeters.
Military Operations
Defence systems use pan-tilt units to mount radar, electro-optical sensors, and thermal imagers. Their precision enables accurate target tracking and situational awareness in real-time missions.
Industrial Automation
In factories and welding operations, positioners ensure stable, continuous monitoring of processes. This helps detect defects early, maintain product quality, and improve overall efficiency.
Maritime Systems
Onboard ships and offshore platforms, positioners stabilize cameras against constant vibration and rough seas. They provide reliable monitoring for navigation, port security, and offshore asset protection.
Environmental Research
Researchers deploy pan-tilt systems to observe wildlife, monitor weather instruments, and track natural phenomena. Their flexibility allows data collection in remote and often extreme environments.
Future Trends in Pan-Tilt Positioners
The future of pan-tilt positioners lies in smarter, lighter, and more connected systems. AI-enabled auto-tracking is making it possible to detect and predict movement without manual control, while advancements in lightweight, high-strength materials are improving portability without sacrificing durability.
At the same time, IoT and cloud integration are enabling remote access, centralized control, and advanced analytics. Beyond traditional monitoring, these innovations are opening new applications in renewable energy, where positioners are being used for solar panel tracking and wind turbine monitoring.
Final Words
Pan-tilt positioners are more than just mechanical mounts, they are precision systems that enable industries to expand their monitoring, inspection, and security capabilities. By understanding key features such as speed, angle range, payload, and material durability, organizations can select the right solution for their environment.
Whether it’s defence, industrial inspection, marine monitoring, or scientific research, pan-tilt positioners provide the flexibility and reliability needed for today’s complex applications.
