Enter your details below to download the product catalogue.
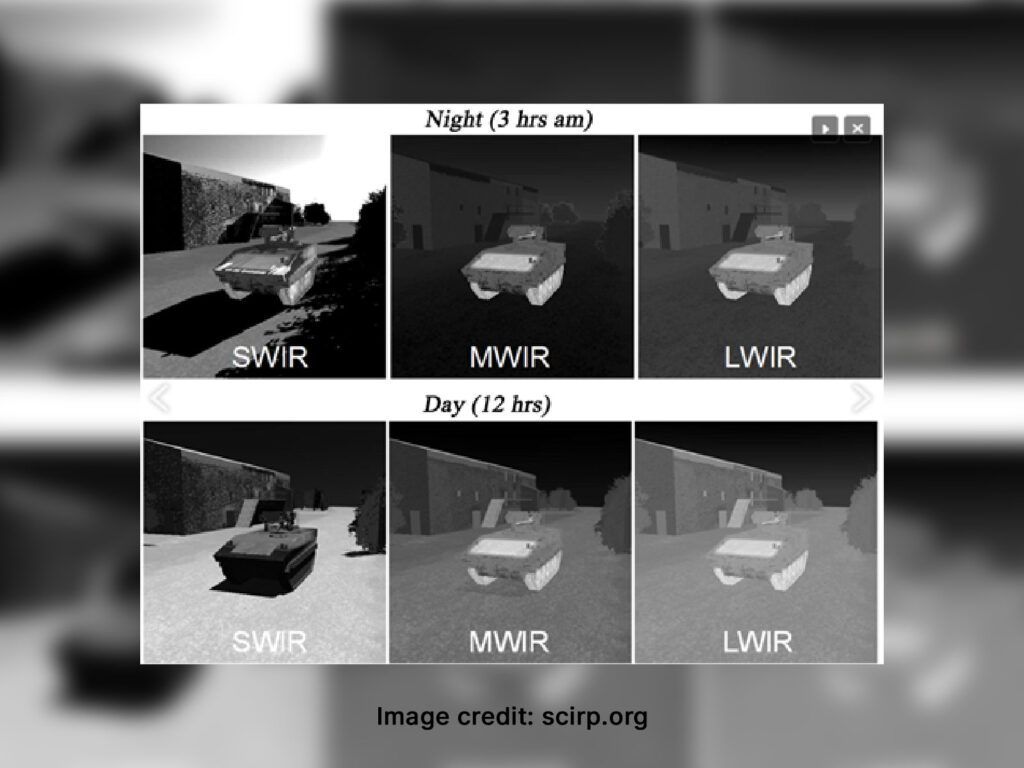
SWIR vs MWIR vs LWIR Cameras: Tech Specs Comparison & Applications Infrared imaging is now an essential part of modern machine vision, industrial monitoring, defence systems, and surveillance. But while most people refer to “thermal cameras” broadly, the reality is that infrared imaging spans multiple wavelength bands, each with different behaviours, advantages, and limitations. The three most widely used infrared categories are SWIR (Short-Wave Infrared), MWIR (Mid-Wave Infrared) and LWIR (Long-Wave Infrared). Understanding how these technologies differ can help you make the right choice for your project, whether it’s inspection, temperature measurement, environmental monitoring or security. Understanding the Infrared Spectrum Infrared light sits just beyond the visible spectrum, but it covers several atmospheric transmission windows. These windows influence how deeply each wavelength can penetrate fog, dust, glass, silicon or moisture. SWIR: 0.9 to 1.7 μm (sometimes up to 2.5 μm) MWIR: 3 to 5 μm LWIR: 8 to 14 μm Each region behaves differently. SWIR relies on reflective imaging similar to visible light. MWIR and LWIR detect emitted heat, but MWIR is more sensitive to fast temperature changes, while LWIR excels in general thermal detection. How Each Camera Type Works…